MSc Healthcare
INSEEC’s Master of Science in Health trains highly sought-after managers of healthcare establishments, ready to head up hospital and medico-social structures from Paris to Lyon, via Bordeaux.
- Obtain an RNCP level 7 qualification
- Manage strategic healthcare facilities
- Master hospital and medico-social management
- Rapid access to management positions

employing structures in the medico-social field
Employment growth in the healthcare sector
Professional integration rate
Average annual remuneration for a health executive
What is a Master of Science in Health at INSEEC?
INSEEC’s Master of Science in Health prepares you to work in a strategic sector undergoing major change, where economic performance, quality of care and organisational innovation must go hand in hand.
This programme is designed for people who want to manage healthcare establishments by putting people at the heart of their decisions. It combines management, health law and work-study to offer a comprehensive view of hospital management. You will develop key skills in budgetary and regulatory management, management of multidisciplinary teams, quality and certification. You will also learn how to manage transformation projects and optimise patient care in a complex and demanding environment.
Available on the Paris, Bordeaux, Lyon, Rennes, Marseille and Toulouse campuses, this MSc is based on specific local features: hospital management in Paris, a medical centre of excellence in Lyon and innovation in e-health in Bordeaux. It provides access to management positions such as hospital director, EHPAD director, clinic director or health project manager.
This programme covers all the major areas of healthcare management to prepare you for the human, economic and organisational challenges of the sector. Find out more below.
Hospitals and Clinics
Management and care
Hospital and clinic management is at the heart of healthcare management. This specialism trains you to manage complex structures, multi-disciplinary teams and quality of care. You will learn how to reconcile economic performance with a public service mission.
You will be familiar with hospital budget management, medico-administrative management, HAS certification, care pathway management and negotiation with supervisory bodies (ARS, Assurance Maladie). You will also learn how to manage restructuring projects, optimise technical facilities and manage relations with the medical profession.
These skills will prepare you for positions as hospital director, MCO or psychiatric clinic director, specialised centre director or hospital project manager in public, private for-profit and ESPIC establishments.
Medical, social and independent living
Supporting vulnerable people
The medico-social and autonomy sector is responding to the challenges of ageing and disability. This specialisation trains you to manage care and support structures, to manage care and entertainment teams, and to develop person-centred projects. You will learn how to create caring and effective environments.
You will be developing skills in the management of nursing homes and senior residences, the running of establishments for the disabled (FAM, IME, ITEP), the management of homecare services (SSIAD, HAD) and the development of establishment projects. You are also familiar with medico-social financing, regulatory assessments and dialogue with families and guardians.
This expertise opens the door to positions as director of nursing homes, director of medico-social establishments, head of home help services or head of autonomy projects in associations, private groups and local authorities.
Health Innovation and Transformation
Modernising and optimising
Innovation and transformation in healthcare place organisations at the heart of changes in the system. This specialism trains you to manage modernisation projects, deploy digital tools and improve the quality and safety of care. You will learn how to make innovation a lever for performance and attractiveness.
You will be familiar with the roll-out of e-health solutions (electronic patient records, telemedicine, connected objects), the management of quality and certification processes, the optimisation of patient pathways and risk management. You will also learn how to manage organisational transformation, develop outpatient services and build coordinated care networks.
These skills will prepare you for positions as quality director, e-health project manager, care network director or innovation director in innovative establishments, GHTs and regional health agencies.
Skills developed
- Defining the health strategy
- Managing a business
- Managing hospital budgets
- Managing multidisciplinary teams
- Leading the digital transformation
- Guaranteeing the quality of care
- Negotiating with supervisory authorities
- Optimising patient pathways
Our training courses
INSEEC Masters of Science in Health
A sandwich course that prepares you for strategic careers in the management of healthcare establishments. Discover the Master of Science in Health and build your expertise in this fast-changing sector.
Campus
-
- 1st year postgraduate
- 3rd year undergraduate
MSc Director of Healthcare Establishments
The professions
Career opportunities for a Master of Science in Health
The Master of Science in Health provides access to strategic management positions in hospitals and medico-social establishments, with rapid integration and attractive career prospects.
Study in the heart of France’s major cities
Our campuses



Campus de Lyon
Take advantage of a historic campus in the heart of Lyon, one of France’s most dynamic cultural and student cities.



Campus de Paris
Discover three modern, easily accessible campuses in iconic Paris locations.



Campus de Bordeaux
Join a modern, friendly campus on the banks of the Garonne, in the heart of a lively, friendly city.



Campus de Rennes
Join a recently refurbished campus in a welcoming, student-friendly town where the energy of Brittany can be felt every day.



Campus de Toulouse
Study on a bright, modern campus close to the centre and Toulouse’s dynamic economy.
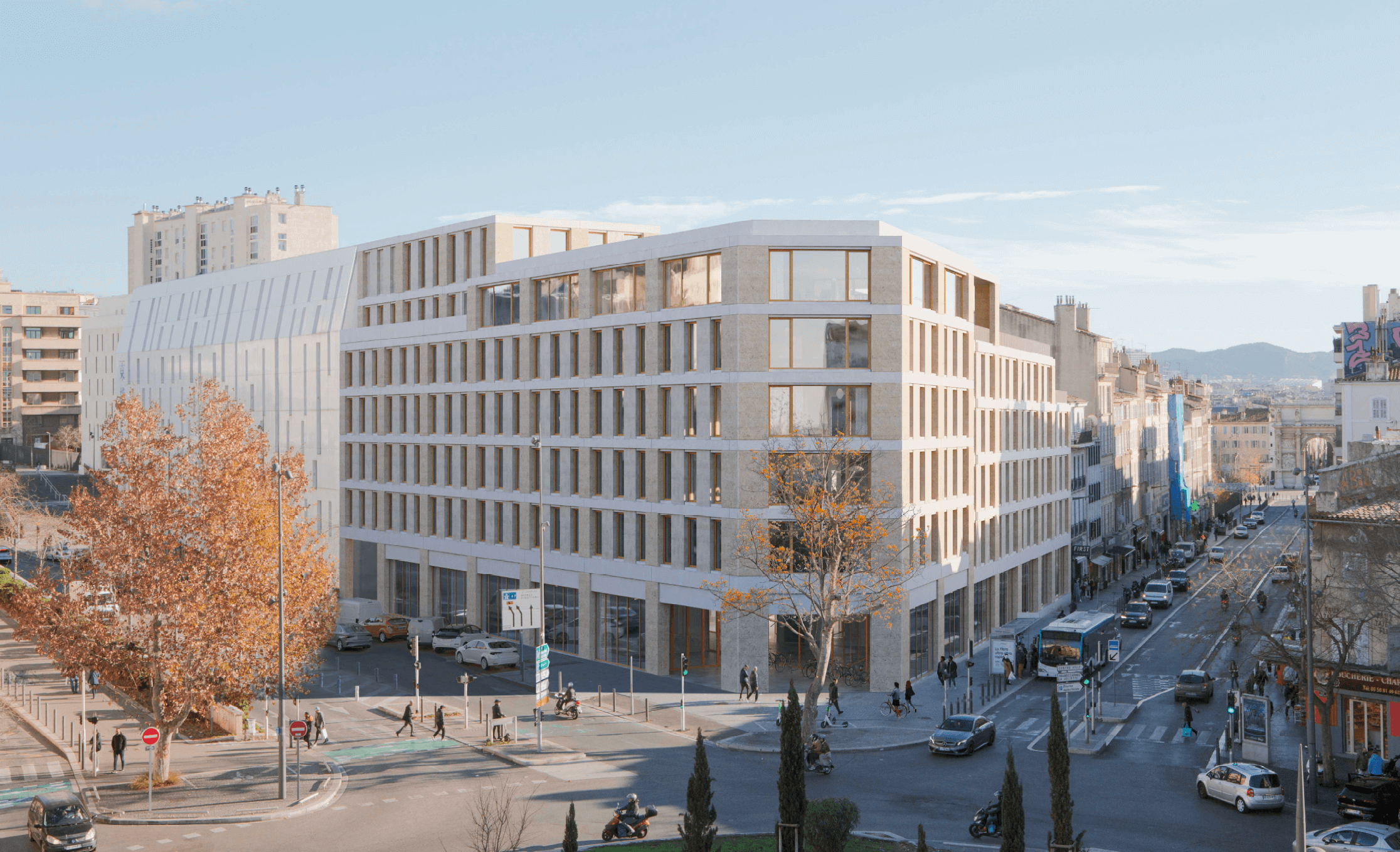



Campus de Marseille
Discover a brand new campus in the heart of Marseille, an energetic Mediterranean city full of contrasts.
Visit us at
Our events
Event type
Campus
-
MSc
03/03
Campus Days in Online
-
MSc
04/03
Open House Days in Online
-
MSc
07/03
Open House Days in Chambéry
FAQ
Questions about INSEEC’s Masters of Science in Health?
The top questions asked about INSEEC’s Health specialisation. And if you haven’t found all your answers here, we’d be delighted to hear from you!
Questions about our Health programmes
Is healthcare a sector for the future?
Absolutely. The ageing population, growing care needs and technological innovation are creating a strong demand for trained facility managers.
- Hospitals, clinics and medico-social establishments are actively recruiting to steer their transformation and meet the challenges of quality care. The sector is undergoing rapid change with the development of e-health, ambulatory care and coordinated care pathways.
- Degrees in this field open up prospects in a variety of activities: public health, private for-profit, medico-social and consultancy. New professions are emerging in clinical research, market access and the development of innovative projects.
- The teaching provided prepares students for the major changes taking place in the French healthcare system. The course enables students to acquire knowledge in management, the healthcare business model and management, enabling them to hold strategic management positions in a buoyant sector.
Do you need a medical background to succeed in the Master of Science in Health?
No, you don’t need to have studied biology, pharmacy, dentistry or medicine. The Master of Science in Health is open to a wide range of people with backgrounds in management, business, law or the humanities, who have completed 3 or 4 years of higher education.
- While knowledge of biology, pharmacy or the healthcare system is an asset, the programme allows you to gradually acquire the necessary expertise.
- The aim is to train managers capable of talking to healthcare professionals, not doctors.
- What counts most is your ability to manage, your organisational skills and your interest in public health issues. A presentation of your background and a solid covering letter are essential for admission.
- The experience gained during the year, through work placements or sandwich courses in different establishments, gives you a real insight into how these establishments operate.
What soft skills are developed with the INSEEC Master of Science in Health?
In addition to the technical skills in hospital and medico-social management acquired during the course, you will develop essential human qualities: the ability to listen and understand the needs of care teams and patients, the ability to manage stress in demanding environments, and the empathy needed to deal with sensitive situations.
- You will strengthen your leadership skills to manage multidisciplinary teams (nursing, administrative, technical), your diplomacy to negotiate with supervisory authorities and partners, and your agility to adapt to regulatory changes.
- The programme also enables you to develop rigour in budget management, to optimise business models and your creativity to propose innovative solutions.
- The soft skills developed during the year of study are crucial to success in the management of healthcare establishments and to progressing to strategic positions in different structures. The job description for a hospital director requires a high level of these cross-disciplinary skills.
Are there any professional speakers or experts from the sector?
Absolutely. The programme includes working professionals from hospitals, clinics, nursing homes and regional health agencies.
- These speakers bring their practical experience to bear through hands-on lessons, real-life case studies and crisis or project management simulations. They share their vision of current issues: digital transformation, quality and certification, patient pathways and management of healthcare teams.
- Some also come from the clinical research, market access or healthcare business development sectors, giving them a comprehensive view of the ecosystem. This proximity to the professional world gives students an insight into the methodologies used in higher education and facilitates access to work-study opportunities.
- Their expertise covers a wide range of activities in the healthcare sector and will be a real asset to your project.
- Each lecturer’s presentation sheet is available at the beginning of the year, detailing their level of expertise and professional title. The course thus benefits from a strong grounding in the field, enabling students to acquire directly applicable knowledge.
Are the healthcare professions really recruiting young graduates?
Yes, health and medico-social establishments are actively looking for young talent to renew their management teams and bring a fresh perspective to management. Young graduates quickly find jobs within months of obtaining their qualifications.
- Work-study programmes and integrated internships facilitate this integration: the vast majority of graduates are hired at the end of their contract.
- Structures are looking for people who have been trained in the realities of the field, and who are able to understand the codes of hospital management and innovative practices. New positions are being created in the development of innovative projects, clinical research and market access.
- Whether it’s in nursing home management, clinic management, quality project management or medico-social management, there are plenty of opportunities for those who know how to combine theoretical knowledge with skills acquired in the field.
- The course provides practical experience during the year of training, making it easier to apply to large public and private organisations.
What is the profile of students who successfully complete the Master of Science in Health?
The students who excel in this programme combine organisational skills, an interest in public health issues and the ability to manage complexity. They come from a wide range of backgrounds after 3 or 4 years’ higher education: business schools, universities of law, management, political science or psychology.
- Profiles with previous experience in the healthcare, voluntary or managerial sectors are particularly successful.
- Students with a degree in pharmacy, dentistry or biology can also join the programme to develop their managerial skills.
- What’s important is that you have an appetite for working with teams, a curiosity about the French healthcare system and the ability to make decisions under pressure.
- The objectives of the programme are to train managers capable of combining economic performance and quality of care in a regulated environment.
What is the salary after a Master of Science in Health?
Graduates of the Master of Science in Health can expect to earn attractive salaries at the start of their career, generally between €39,000 and €55,000 gross per annum, depending on the position and the structure. Deputy directors of nursing homes and project managers in nursing homes start out in this range.
- After 3 to 5 years’ experience as director of a medium-sized nursing home, director of a medical-social centre or hospital quality manager, remuneration ranges from €50,000 to €82,000. Experienced candidates with positions as hospital director, director of a large clinic or director of a medical-social group in large facilities can earn €75,000 to €110,000 and more.
- Positions in business development, market access or clinical research also offer attractive packages. Private for-profit establishments and commercial groups generally offer higher levels of remuneration than the public sector.
- Salary progression is gradual for profiles who have mastered strategic steering, budget management and team management. The job description for each function indicates salary levels according to experience and job title.
How can I finance my Master of Science in Health?
There are several ways of financing this year’s training. Work-linked training or apprenticeships remain the most advantageous solutions: most of your tuition fees are paid by the employing establishment, and you receive a salary while gaining practical professional experience in a healthcare organisation.
- The course can also be taken as an initial course, with long-term placements in hospitals, clinics or nursing homes. You can take out preferential-rate student loans with our preferred partners.
- Work-linked applications are particularly encouraged, as they allow you to acquire knowledge while being paid during your course.
- This offers an excellent training opportunity, while immersing you in different activities in the health and medical-social sector instead of a purely theoretical course.
Is it possible to work abroad with the INSEEC Master of Science in Health?
Yes, healthcare management skills are in demand internationally, particularly in global healthcare organisations and multinational hospital groups.
- Many courses include an international dimension on comparative healthcare systems, intercultural management and international quality standards.
- You can do your placements in clinics abroad, in organisations such as the WHO or in groups operating on several continents. French diplomas in healthcare management are recognised in different geographical areas.
- Students work in organisations in Europe, French-speaking Africa and the Middle East, managing multicultural establishments and managing projects with an international dimension. New markets are opening up in the development of market access solutions and international clinical research.
- Fluency in English is an asset for these careers, where you will be required to apply for management positions in a variety of contexts.
- International students on the programme bring their network and knowledge of different systems.
Can the Health specialisation be taken into parallel admission?
Yes, parallel admission is possible for candidates with a validated Bac +4 or significant experience in the healthcare field. You can enter the second year of the Master of Science (MSc 2) directly, depending on your previous experience and qualifications, by submitting an application and covering letter.
- The admissions process assesses your academic record, your professional or community experience in the healthcare sector and your career plans. An interview ensures that your profile matches the objectives of the programme.
- Applications are examined individually to identify students with the potential to succeed in this demanding course. This flexibility means that we can take on a wide range of students from a variety of backgrounds: business schools, universities of management, health law or political science.
- Graduates in pharmacy, dentistry or biology can also join the programme to develop their business and management skills. International students are encouraged to apply, as their international backgrounds will enrich the group.
- The admissions form sets out the levels required, the qualification sought and the documents needed to apply and join this course, which is geared towards the new challenges facing the sector.